
Lactose-N-neotetraose
Control Substance.
- CAS Number 13007-32-4
- Package:50mg, 250mg, 1g
- Function: Special low-level polymeric sugars added to formulas for promoting intestinal health and immunity.
- Application: Used in milk powder, food, and other formulas to imitate breast milk components.
- Tags:
Featured products
Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) are unique low-level polymeric sugars added to milk powder, food, and other formulas to emulate the nutritional components and bioactive molecules present in breast milk. This addition aims to comprehensively enhance intestinal health, immune system development, and overall well-being. Through interactions with microorganisms, HMOs generate beneficial metabolites, fortify intestinal barrier function, and mitigate intestinal inflammation. Simultaneously, they regulate the balance of intestinal flora, foster the growth of probiotics, and sustain intestinal health.
Basic Information
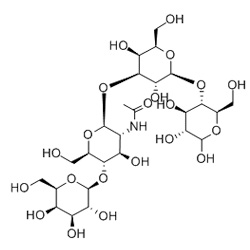
Molecular Formula: C26H45NO21
Molecular Weight: 707.62
Usage: 0.5-8.5g/Kg
Human Milk Oligosaccharide Composition:
Human milk oligosaccharides consist of five monomers (D-glucose, D-galactose, N-acetylglucosamine, L-fucose, and N-acetylneuraminic acid or sialic acid), combined in varying proportions.
Classification of Human Milk Oligosaccharides
HMOs can be categorized into neutral human milk oligosaccharides (Neutral HMOs) and acidic human milk oligosaccharides (Acidic HMOs). Neutral HMOs contain a fucose group, while acidic HMOs include a structure with sialic acid and its sulfate. Over 200 types of oligosaccharides have been identified in human milk.
Application and Functions of Human Milk Oligosaccharides in Infant Food
Currently, two types of HMOs approved for use in infant formula are 2-fucosyllactose (2’-FL) and lacto-N-neotetraose.
Pathogen Prevention: Acts as a guardian for the infant's intestines by preventing pathogens from attaching to epithelial cells.
Intestinal Health: Promotes the maturity of intestinal mucosa and the barrier function of intestinal epithelium, acting as a regulator for intestinal epithelial cells and balancing microbial flora.
Immunomodulation: Functions as a prebiotic, directly and indirectly regulating immune cells and serving as an immunomodulator.
Mineral Absorption: Reduces the pH value of the colon, facilitating the absorption of minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and iron.
Nutritional Support: Provides essential nutrition required for the growth and development of infants.
Customers Also Viewed




